Socket Stream Extension
Socket Stream enables remote control of OCTproZ and allows streaming of processed data to another application, either on the same computer or on a different computer within the same network.
Supported communication protocols are: TCP/IP, WebSocket and IPC. IPC is implemented using Qt's QLocalServer and QLocalSocket, which use Unix Domain Sockets on Linux and Named Pipes on Windows.
One example use case is transferring OCT data to a Python application for post-processing.
Another example is remotely controlling a small, portable OCT system that either has no display or only a limited display, via a smartphone or tablet.
How to use
-
Create a custom client application (see Python examples here)
or use this WebSocket client that runs in a browser. -
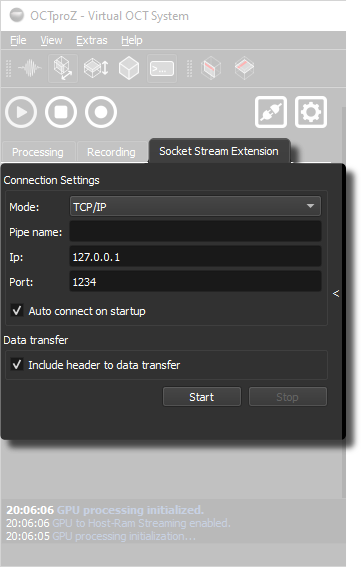
Set the communication protocol, IP, and port (or the pipe name in case of IPC) in the Socket Stream extension.
-
Click Start to start the server.
-
Connect your client to the server using the configured IP and port.
-
If you want to stream image data to your client, it is recommended to connect a second client: Use one client for commands only (activate with the command
enable_command_only_mode)
and a second client for image streaming only. -
Use commands (see table below).
User interface
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Mode | Selects the communication protocol: TCP/IP, IPC (Local Sockets), or WebSocket. |
| Pipe name | Name of the IPC pipe (used only in IPC mode). |
| IP | IP address of the server (used in TCP/IP and WebSocket modes). |
| Port | Port number of the server (used in TCP/IP and WebSocket modes). |
| Auto connect on startup | Automatically starts the server when the extension is activated. |
| Include header to data transfer | Adds a 13-byte header to every data packet containing meta information like image size and bit depth. |
Data header
If enabled, each transmitted data packet starts with a 13-byte header containing meta information about the OCT image. This allows the client to correctly interpret the incoming data.
The header consists of:
| Field | Type (Size) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Magic Number | unsigned int (4 bytes) | Fixed value 299792458 (decimal) for synchronization |
| Data Size | unsigned int (4 bytes) | Total size of image data in bytes |
| Frame Width | unsigned short (2 bytes) | Number of pixels per A-scan |
| Frame Height | unsigned short (2 bytes) | Number of A-scans per frame |
| Bit Depth | unsigned char (1 byte) | Bits per pixel (e.g., 8 or 16) |
Available remote commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
remote_start |
Starts the OCT processing. |
remote_stop |
Stops the OCT processing. |
remote_record |
Starts recording the OCT data. |
load_settings:<path_to_settings_file> |
Loads settings from a specified file. Replace <path_to_settings_file> with the actual file path. |
save_settings:<path_to_settings_file> |
Saves current settings to a specified file. Replace <path_to_settings_file> with the desired file path. |
set_disp_coeff:<coeff1>:<coeff2>:<coeff3>:<coeff4> |
Sets dispersion coefficients. Each value can be a double or nullptr / null. |
set_grayscale_conversion:<enable_log_scaling>:<max>:<min>:<multiplicator>:<offset> |
Configures grayscale conversion. Parameters: enable_log_scaling (true/1 or false/0), the rest are double values or nan / null / nullptr. |
remote_plugin_control,<PluginName>,<Command> |
Sends a command to another OCTproZ plugin. Example: remote_plugin_control, Dispersion Estimator, startSingleFetch |
enable_command_only_mode |
Switches client connection to command-only mode (no image streaming). |
disable_command_only_mode |
Switches client connection back to command + data streaming mode. |
ping |
Health-check command — server replies with pong. |